TNA project : Exploration of the robot hand grasping abilities using haptic devices
Acronym : 84-Exploration of the robot hand grasping abilities using haptic devices-Kumicakova
Project Lead : Darina Kumicakova From : University of Zilina, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Dates : from 2nd April 2013 to 14th April 2013
Description :
Motivation and objectives :
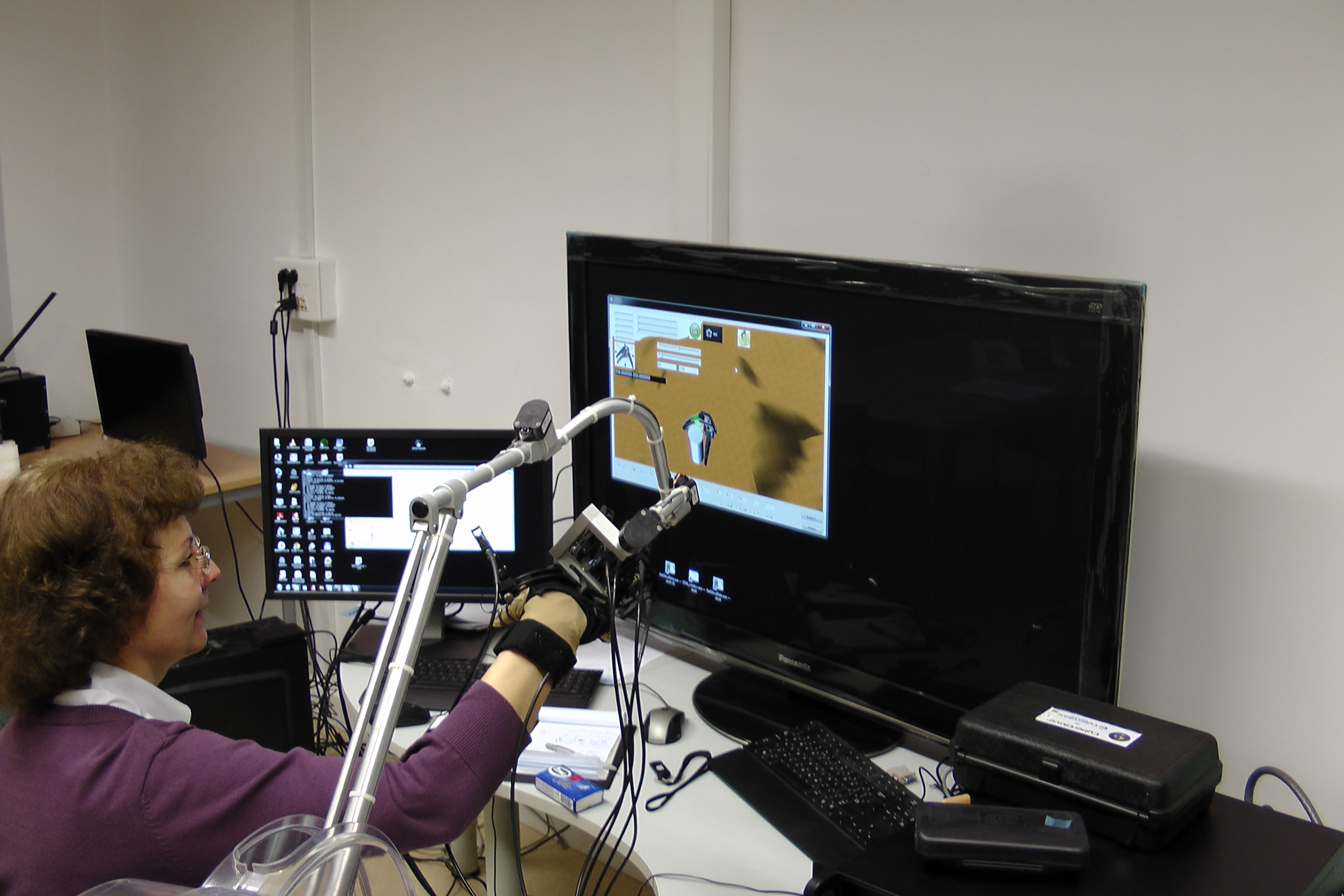
Robot hands or robotic end-effectors are of different type but every of them are designed in order to mimic more or less capabilities of the human hand to manipulate with objects of different shape and dimensions. Human grasps any object intuitively by that way in order to make it stable. Artificial hand must be specially controlled to do it. Its design and dexterity is possible to verify by simulation in currant available CAD/CAM/CAE systems virtual environment by more or less complicated ways. Another way is an utilisation of the specialised simulation software or devices (haptic devices) which are usually of a high cost of acquisition. Haptic feedback is a recent addition to Virtual reality (VR) simulation. This sensorial modality increases the simulation realism during virtual object grasping/manipulation and enables to test the robot hand dexterity in VR environment. In this context, the main objective of this research project is utilisation of CyberForce haptic devices for the robot mechanical hand (RMH) design verification. The attention is aimed to a testing of the RMH ability to grasp various objects.
Teams :
Department of Automation and Production Systems was founded 01.01.2009 in framework of the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering structure reorganization. Before this date the majority of the department staff was member of the Division of Automation at other departments of Faculty of Mechanical Engineering (approximately from the year 1988). At the present the department operates 1 Professor, 4 Associated professors, 1 Assistant professor, 3 researchers, 6 PhD. students of daily study form, 4 PhD. students of external study form and 2 technicians. Department focuses on the issues of computer support and automation in the engineering industry with an emphasis on programming NC and CNC production machines and industrial robots, work with CAD, CAD/CAM, CAD/CAE, CAPP and CAQ systems, solving of technical production preparation with using CAx systems and technologies and application of microelectronics and microcomputers in engineering practice.
Dates :
starting date : 02 April, 2013
ending date : 14 April, 2013
Facilities descriptions :
http://visionair-browser.g-scop.grenoble-inp.fr/visionair/Browser/Catalogs/VDS.PL.html
Recordings & Results :
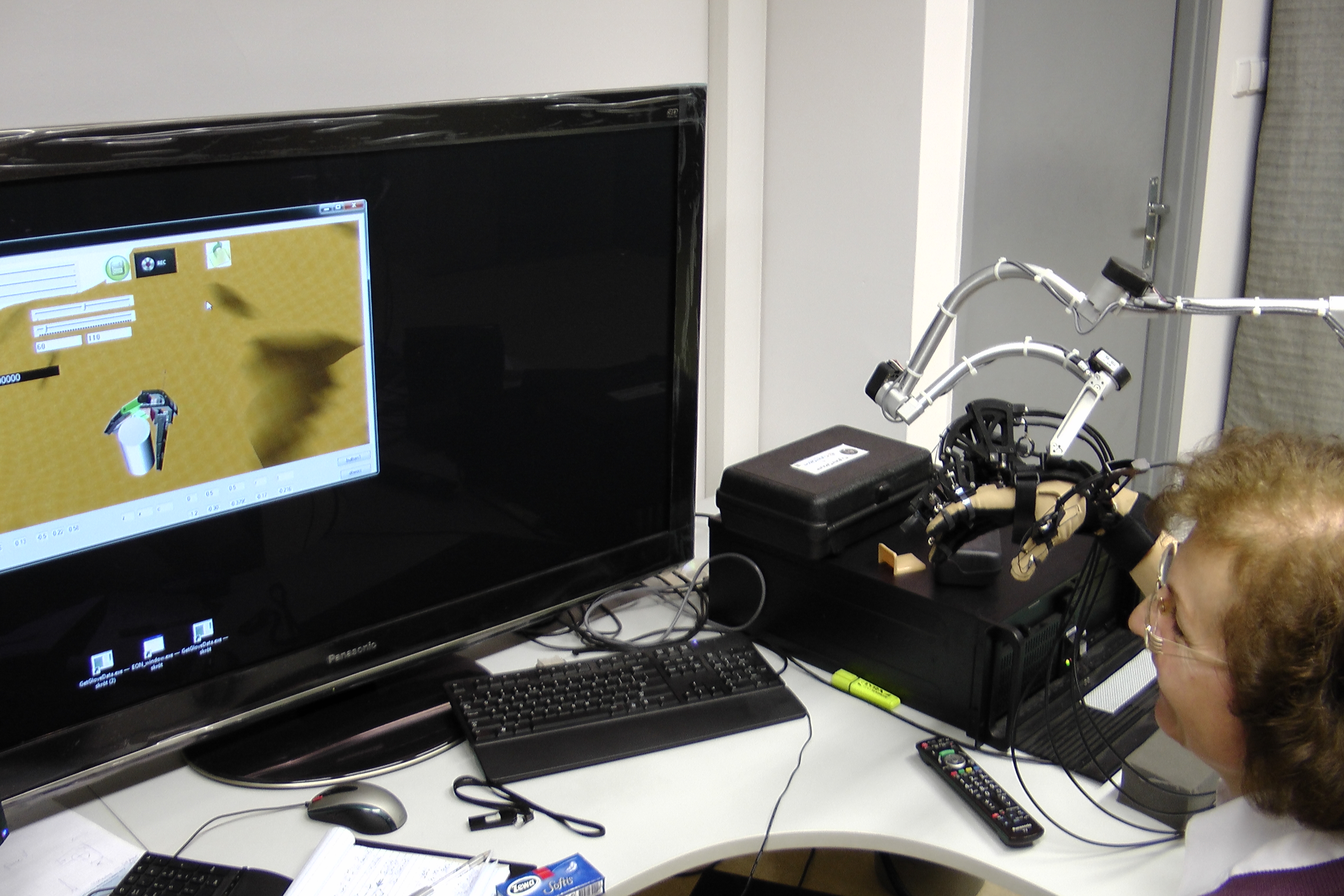
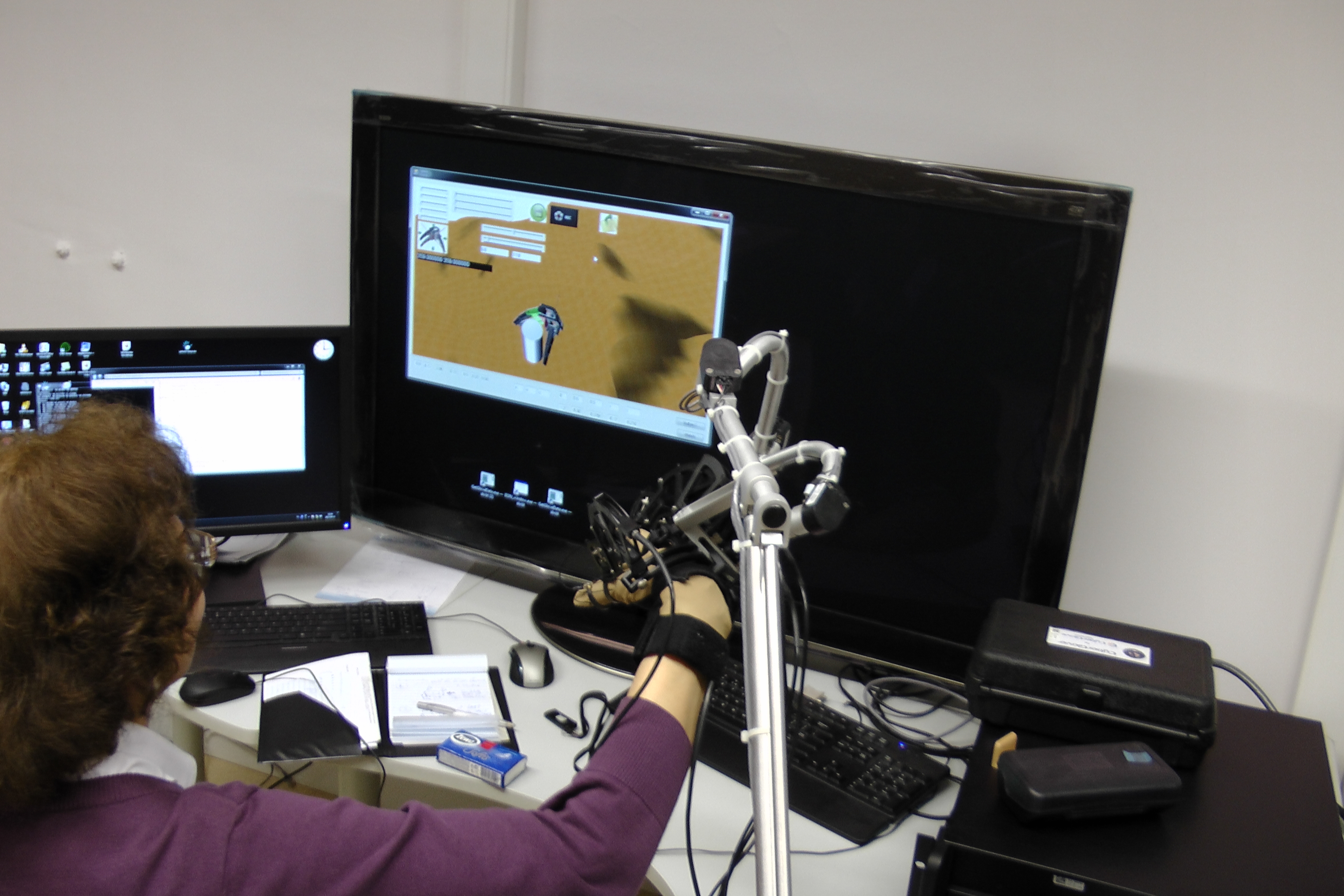
Work description: 1. Preparation of RH and object models (cylinder, cube and assembly part) for the simulations executed by help of both the keyboard and the CyberForce device: • definitions of rigid bodies – RH as a kinematic body, grasped objects as dynamic bodies (affected by the kinematic body), environment as a static body • definition of the RH´s self-collision detection (Fig. 1 in Table, other colour display) • definition of the RH and grasped object collision detection (Fig.2 in Table, other colour display) • setting of restrictions for movement of both 2nd and 3rd joints of RH´s every finger These conditions were needed for more realistic simulation of the object grasping and had to be improved gradually. A lot of supporting experiments had to be executed. 2. Simulation of the cylinder grasping execution. To obtain more information about RH´s grasping ability of objects of the cylinder type, the conditions were variable: the cylinders of various dimensions were tested (D = 40, 60, 80, 110 and 120mm, h = 110mm or h = 10mm) – see Fig. 3, 4 and various ways of their grasping were tried– see Fig. 4, Fig. 4_1. 3. Some simulations of the other object grasping were executed too. We have used: the prism with a square cross-section a x a (a = 50, 60 and 70mm) and with a height h = 60, 80 and 110mm and the assembly part - see Fig. 5_1.
Conclusions :
Experiments were executed using both ways of RH control – by keyboard and by the CyberForce device utilisation. Results of each simulation were recorded in the form of: “.txt” files and files of the simulation process screenshots. The RH is able to grasp objects of cylinder shape of diameter range from 40 up to 110 mm and of height from 60 up to 110mm or higher. Object is well grasped thanks to possibility of its stabilisation in the RH´s palm element. The RH´s possibilities to grasp cylindrical objects in another way are very limited. Grasping of objects of other shape or small dimensions is limited too (diameter or cross-section < 30mm).
Few images :


.
VISIONAIR / Grenoble INP / 46 avenue Felix Viallet / F-38 031 Grenoble cedex 1 / FRANCE
Project funded by the European Commission under grant agreement 262044
Project funded by the European Commission under grant agreement 262044