TNA project : Data visualization for the complexity of human resource planning in home health care
Acronym : 29-Data visualization for the complexity of human resource planning in home health care-Ettore
Project Lead : Lanzarone Ettore From : Istituto di Matematica Applicata e Tecnologie Informatiche (IMATI) sezione di Milano, Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche
Dates : from 15th July 2013 to 28th July 2013
Description :
Motivation and objectives :
Home Care (HC) includes medical, paramedical and social services that are delivered to patients in their homes. The purpose of HC is to alleviate the pain of the assisted patients and to improve or sustain their health and quality of life. The main benefit of HC is a decrease in the hospitalization rate, leading to both significant increases in the quality of life for patients and relevant cost savings in the health care system. This service is a relevant and growing sector in the healthcare domain of western countries because of the ageing of the population, the increase in chronic pathologies, the introduction of innovative technologies and the continuous pressure of governments to contain healthcare costs. Many resources are involved in service delivery, including different categories of operators (e.g., nurses, physicians, physiotherapists, social assistants and psychologists), support staff and material resources. Patients are classified into different categories and each category includes a certain number of Care Profiles (CPs) based on specific needs, the level of requirement and the costs associated with the provided services. Patients need to be cared for by different categories of operators: they are always under the charge of the nurses and, in some cases, of other operators. Within each category, operators are divided into districts: they take care of patients belonging to CPs that they are skilled for and, in large HC providers, they are divided into territorial groups and take care (only or preferably, according to the provider policy) of patients who are resident in their territory. Some HC providers pursue the continuity of care, i.e., patients are assigned to only one operator for each category, named reference operator, who follows the entire patient care pathway and preferably provides all of the visits that are pertinent to his/her category. The continuity of care is an important quality indicator of the HC service because the quality perceived by the patient is preserved when he/she receives care from the same person and, thus, he/she does not have to continuously change his/her relationship with a new operator. This project focuses on facilitating and optimizing the planning and management of HC human resources. In detail, these activities include the assignment of patients to their reference operator under continuity of care, the definition of the weekly schedules and the daily management of variations with respect to the schedules. Specifically, the planning of nurses' activities is analyzed. Nurses are chosen because they provide the largest amount of visits to the patients and manage the emergencies and the variations in demand with a high uncertainty of the workload amount. We previously developed a set of methodologies for solving the nurse-to-patient assignment problem, with the main goal of balancing the workloads among the nurses, under the constraint of satisfying the care volume necessary to the patients under the charge and preserving the continuity of care. Moreover, given the necessity of estimating the demand from the patients under the charge during the planning period, a stochastic model that describes the evolution of a patient's conditions and provides estimates on the amount of visits required during his/her stay was also developed. The practical application of the proposed methodology in real cases is considered to be crucially important, in the light of the potential benefits for HC providers and because only a small percentage of the models available in the literature have been implemented in practice. Hence, the approaches developed are applied to the real case of the largest Italian public HC provider. In detail, a module containing the proposed models was included in the managerial software used by this provider, in collaboration with the company that developed this managerial software. However, due to the high amount of data to be managed and shown, the outcomes of the software tool resulted to be poor in terms of completeness and easy manipulation by the planners of the HC human resource activities.
Teams :
The IMATI-MILANO research unit is established within the Milan department of the Institute of Applied Mathematics and Information Technology "Enrico Magenes" of the Italian National Research Council (CNR).
Dates :
starting date : 15 July, 2013
ending date : 28 July, 2013
Facilities descriptions :
http://visionair-browser.g-scop.grenoble-inp.fr/visionair/Browser/Catalogs/MEXICO.FR.html
Recordings & Results :
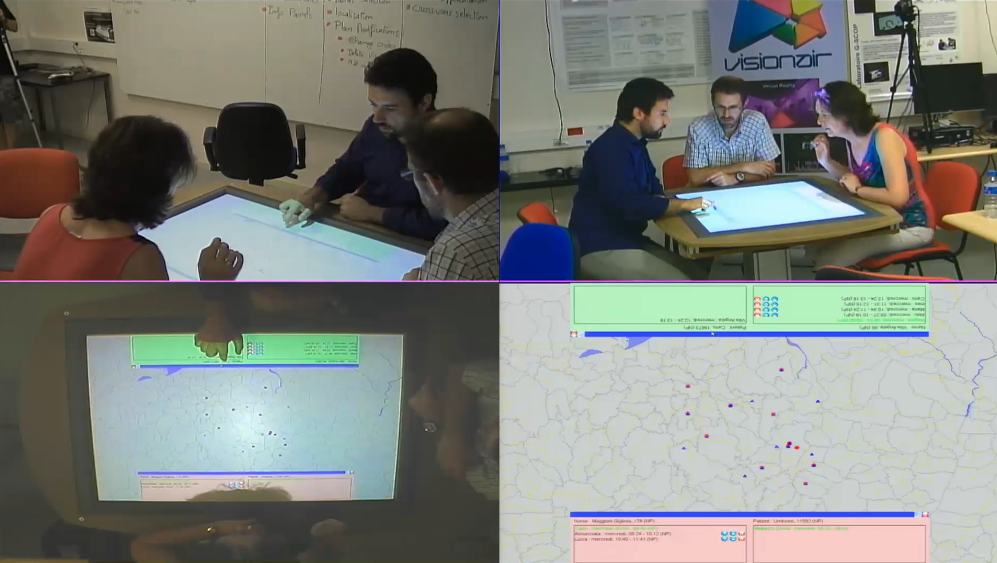
The project aims at defining and implement a new visualization framework that enables HC planners to easily manage the high amount of data related to HC human resource activity planning and to work in team with a real time sharing of information. The challenge is to give the planners all the information in such a way that they could easily manage the data and control the entire assignment process in a coordinated way. In particular, we focus on the daily replannig of nurses' activities: after the definition of the weekly activity scheduling, planners have to daily control the activities of the nurses in order to face the disruptive events that can emerge in the provision of visits. The developed tool consists of an interactive maps, on which the territorial distribution of patients and operators can be show, together with other information in a multilayer configuration. The tool also enables planners to modify the plans while using all the information required for an optimal decision making process.
Conclusions :
A propototype of the tool is successfully implemented. Moreover, the functional validation of the prototypal tool is conducted. Two categories of tests are considered: visualisation and interactions. In the following the defined requirements that are tested are reported. Visualisation : • user is able to visualise the geographic area he is managing • user is able to manipulate the map to adapt the visualisation area (pan, zoom) • user is able to visually distinguish the status of patients, i.e., with visits to be still received in the day (covered/uncovered) or with no visits • user is able to visually distinguish the status of nurses, i.e., in car, at a patient's home, at office • user is able to visually associate the iconic metaphores of patients and nurses to the textual information displayed in the private areas • user can visualize nurse's remaining route for the current day • each user has access to a private area where information related to patient and nurses can be displayed; in particular it is required for nurse to have the daily schedule and for patients to have the list of the visits planned in the day • the user can visualize on the map the issues in the initial planning Interactions : • multiple users (up to 4) are able to make the actions described above • user is able to change the order of the visits that are included in the nurse's list user can erase a visit from a nurse's list • user can add a visit to a nurse's list • user can glide across the time in the simulation (e.g. to anticipate events in the future by displaying the potential state of the system in the day) The basic tasks that could involved this functions are : • a patient is cancelling his visit • a patient asks for modifying his visit schedule • a nurse asks to cancel a visit because of too much delay • the planner want to check the availability of a nurse Finally, the validation tests are recorded and a video is provided to be shown in real home care providers. On one side, this allows to disseminate the outcome of the project for a possible real application in the management of nurse workforce; on the other, this permits to obtain feedbacks and suggestion for further evolution of the propotypal tool.
Few images :

.
VISIONAIR / Grenoble INP / 46 avenue Felix Viallet / F-38 031 Grenoble cedex 1 / FRANCE
Project funded by the European Commission under grant agreement 262044
Project funded by the European Commission under grant agreement 262044