Title : Collision Avoidance with Virtual and Physical Objects During Walking in a CAVE
Project Lead : Gerd Bruder From : University of Wuerzburg (None)
Dates : from -- to 2014-04-30 16:24:42
Description :
Motivation and objectives :
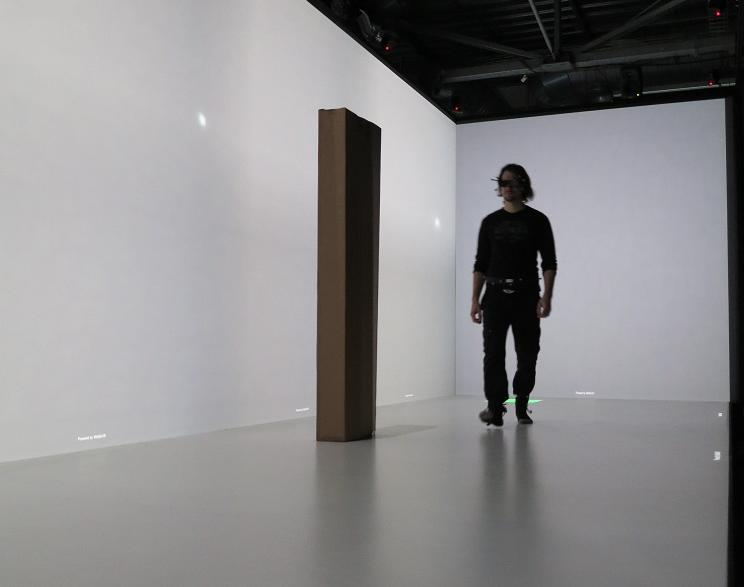
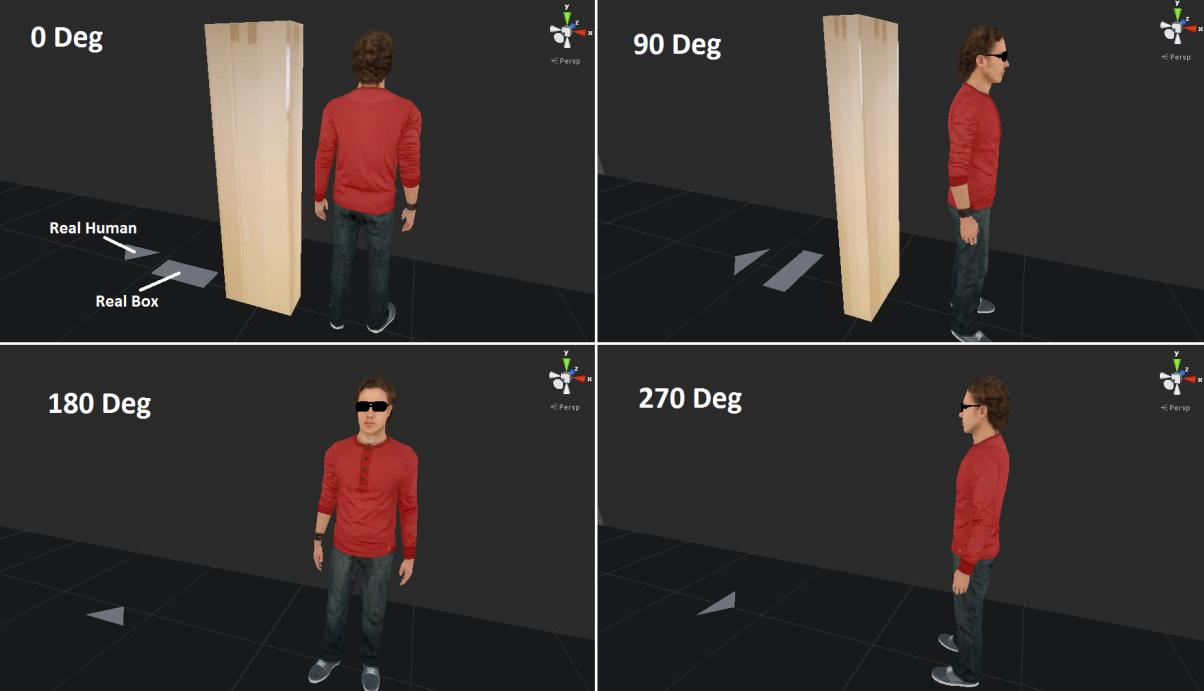
Accurate perception of spatial affordances of virtual objects, which are depicted in an immersive virtual environment (IVE), is important for many application domains. In this project we evaluate the perceptual fidelity of virtual environments (VEs) with respect to how well they convey information about geometry and spatial affordances during natural locomotion in a CAVE. We vary the spatial structure, appearance, and interaction affordances of virtual objects and measure how accurately users are able to perceive action-relevant virtual information. We compare the results to a baseline condition in which we replicate the virtual conditions with real-world objects. Our methodology for evaluating the perceptual fidelity is based on assessing collision avoidance behavior while walking in the presence of virtual and physical objects while perceiving visual body feedback. So far, limited research exists on spatial perception during natural locomotion in CAVEs. The main reasons for this are the small walking areas provided by nearly all existing CAVEs. Fortunately, the CAVE in Rennes provides a 10 meters x 3 meters walking area, which is one of the largest in the world. We make use of this large area to conduct experiments based on real walking in the presence of real and virtual obstacles.
Teams :
The Immersive Media Group (IMG) at the University of Wuerzburg is oriented towards interdisciplinary teaching and research that deals with aspects of information processing in the context of digital media. A special focus is on the area of virtual reality, human-computer interaction in stereoscopic 3D environments, as well as space and motion perception in immersive virtual environments.
Dates :
starting date : 17 February, 2014
ending date : 08 March, 2014
Facilities descriptions :
http://visionair-browser.g-scop.grenoble-inp.fr/visionair/Browser/Catalogs/IMMERSIA.FR.html
Recordings & Results :
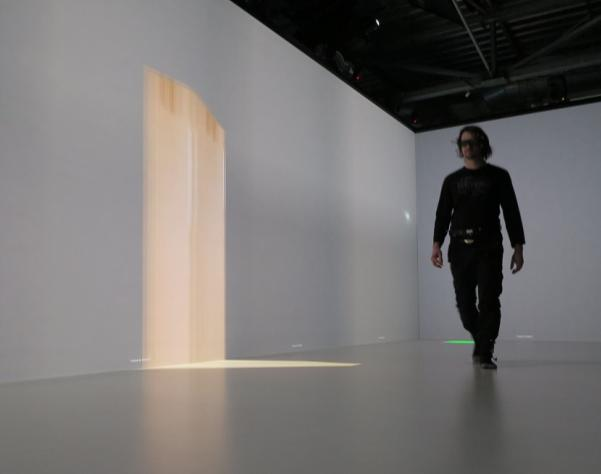
Our main objective in this project was to compare obstacle avoidance behavior between simple real or virtual geometrical objects as well as real or virtual humans with different affordances. We conducted a behavioral dynamics experiment, which revealed different avoidance behavior of participants towards the considered virtual objects compared to their physical counterparts. During additional pilot tests in the large walking area of the IMMERSIA setup we considered different potential contributing factors. We observed differences in distance estimates to virtual objects depending on the position of the observer in the projection setup. In order to formally investigate this factor we conducted a second experiment. The experiment revealed interaction effects between accommodation distances, stereoscopic parallax, and target distance on distance judgments in the projection environment, which provides interesting guidelines and vistas for future research.
Conclusions :
We conducted a behavioral dynamics experiment, which revealed different avoidance behavior of participants towards the considered virtual objects compared to their physical counterparts. During additional pilot tests in the large walking area of the IMMERSIA setup we considered different potential contributing factors. We observed differences in distance estimates to virtual objects depending on the position of the observer in the projection setup. In order to formally investigate this factor we conducted a second experiment. The experiment revealed interaction effects between accommodation distances, stereoscopic parallax, and target distance on distance judgments in the projection environment, which provides interesting guidelines and vistas for future research.
Project Images :



Other project resources :
bruder_visit_report_document.pdf
.
VISIONAIR / Grenoble INP / 46 avenue Felix Viallet / F-38 031 Grenoble cedex 1 / FRANCE
Project funded by the European Commission under grant agreement 262044
Project funded by the European Commission under grant agreement 262044