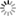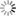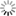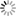Title : 3D Airflow and Heat Exchange Visualization of a Server Room under Various Load Scenarios.
Project Lead : Wojciech Szeliga From : Poznan Supercomputing and Networking Center (None)
Dates : from 2013-09-09 00:00:00 to 2013-09-09 00:00:00
Description :
Motivation and objectives :
Data centers are responsible for around 2% of the global energy consumption mak- ing it equal to the demand of aviation industry. In many current data centers the actual IT equipment uses only half of the total energy while most of the remaining part is required for cooling and air movement resulting in poor Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) values. Large energy needs and significant CO2 emissions caused that issues related to cooling, heat transfer, and IT infrastructure location are more and more carefully studied during planning and operation of data centers. Even if we take ecological and footprint issues aside, the amount of consumed energy can impose strict limits on data centers. First of all, energy bills may reach millions euros making computations expensive. Furthermore, available power supply is usually limited so it also may reduce data center development capabilities, especially looking at challenges related to exascale computing breakthrough foreseen within this decade. For these reasons many efforts were undertaken to measure and study energy efficiency of data centers. In order to optimize a design or configuration of data center we need a thorough study using appropriate metrics and tools evaluating how much computation or data processing can be done within given power and energy budget and how it affects temperatures, heat transfers, and airflows within data center. In particular, there is a need for simulation tools and models that approach the problem from a perspective of end users and take into account all the factors that are critical to understanding and improving the energy efficiency of data centers, in particular, hardware characteristics, applications, management policies, and cooling. To address these issues the CoolEmAll project (coolemall.eu) aims at decreasing energy consumption of data centers by allowing data center designers, planners, and administrators to model and analyze energy efficiency of various configurations and solutions. To this end, the project works on models of data center building blocks and tools that apply these models to simulate, visualize and analyze data center energy efficiency. Recently, the applicant has been working on CFD simulation of an airflow and heat exchange based on server room owned by Poznan Supercomputing ang Networking Center. Goal was to investigate hot spots, main trends and plan eventual modifications to improve cooling effectiveness. 3D visualization made with CAVE in HLRS of gained results could help with drawing proper conclusions. Plan for the future is to populate the server room with CHRISTMANN RECS servers, what generates a need to prepare CFD simulation of new configuration to plan the new set properly. Mostly desired are informations about trends caused by cloud and high performance computing loads. Extraction of searched data could be done in cooperation of PSNC and HLRS. Linking all data gained by PCNS with recent empirical measurements of single RECS and detailed data about server room with HLRS' experience of 3D visualization could give a chance to prepare together a set of simulations of different loads and visualize them in a closer to human's perception way than a standard visualization. Visualizations prepared within the project will provide a better insight into heat transfer and airflow processes in a data center, and, consequently, will provide means to improve data center energy efficiency taking into account specific workloads.
Teams :
Advanced applications and computing are exciting research areas that study how to use high performance and distributed compuers, storage and optical networks in an efficient and easy-to-use way from the end users perspective. Applications Department Group at Poznan Supercomputing and Networking Center consists of an elite team of experts whose expertise covers a wide spectrum of research and devlopment activities conducted in regional, national and international multi-disciplinary projects. With the scope of information and communication technologies, we help our users to take advantage of innovative IT infrastructures, services, platforms, applications and human-computer interfaces. All the applications have been desgined and developed in close collaboration with various partners over the last decade and can be applied to both natural and social scientific fields.
Dates :
starting date : 01 August, 2013
ending date : 12 August, 2013
Facilities descriptions :
http://visionair-browser.g-scop.grenoble-inp.fr/visionair/Browser/Catalogs/HLRS.GE.html
Recordings & Results :
To address these issues the CoolEmAll project (coolemall.eu) aims at decreasing energy consumption of data centers by allowing data center designers, planners, and administrators to model and analyze energy efficiency of various configurations and solutions. To this end, the project works on models of data center building blocks and tools that apply these models to simulate, visualize and analyze data center energy efficiency. Recently, the applicant has been working on CFD simulation of an airflow and heat exchange based on server room owned by Poznan Supercomputing ang Networking Center. Goal was to investigate hot spots, main trends and plan eventual modifications to improve cooling effectiveness. 3D visualization made with CAVE in HLRS of gained results could help with drawing proper conclusions.
Conclusions :
3D visualization of mentioned simulation of PSNC server room was successfully performed. Below can be seen attached pictures taken from used CAVE infrastructure. To get close to real-world contitions, visual model of a server room was made with usage of pictures taken inside the server room. Imposed CFD results, where load of rack units were differed, provided informations about air sucked by the racks (proportions of amounts gained by air conditioning and hot air coming from racks). It turned out that the proportion is not satisfactory. Causes may be two. One is too small velocity of cooling air coming from floor inlets, which points that power of cooling needs to be increased. Second cause may be connected with deviations of measurements deviations, as the stream is turbulent. Another informations received from computed data are details of unplanned migration of warmed air to cold corridors, which gave the answer how additional curtains should be set in the PSNC server room to improve cooling efficiency.
Project Images :

.
VISIONAIR / Grenoble INP / 46 avenue Felix Viallet / F-38 031 Grenoble cedex 1 / FRANCE
Project funded by the European Commission under grant agreement 262044
Project funded by the European Commission under grant agreement 262044